More than 9,000 video lectures across 16 subjects
The benefits of using MASSOLIT at your school
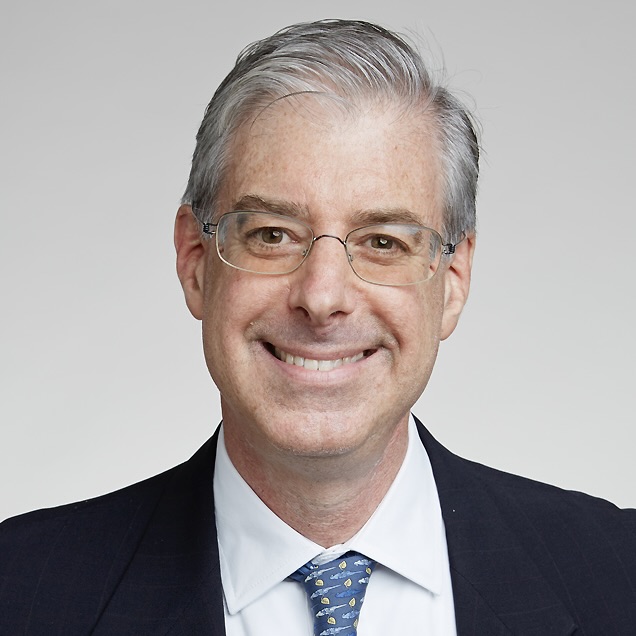
English Literature
Lecture
Scene 1 (17:34)
Prof. John McRae, Nottingham University
Subject knowledge CPD for you and your team
Build your subject knowledge with our library of more than 9,000 short video lectures, each one presented by a university academic.
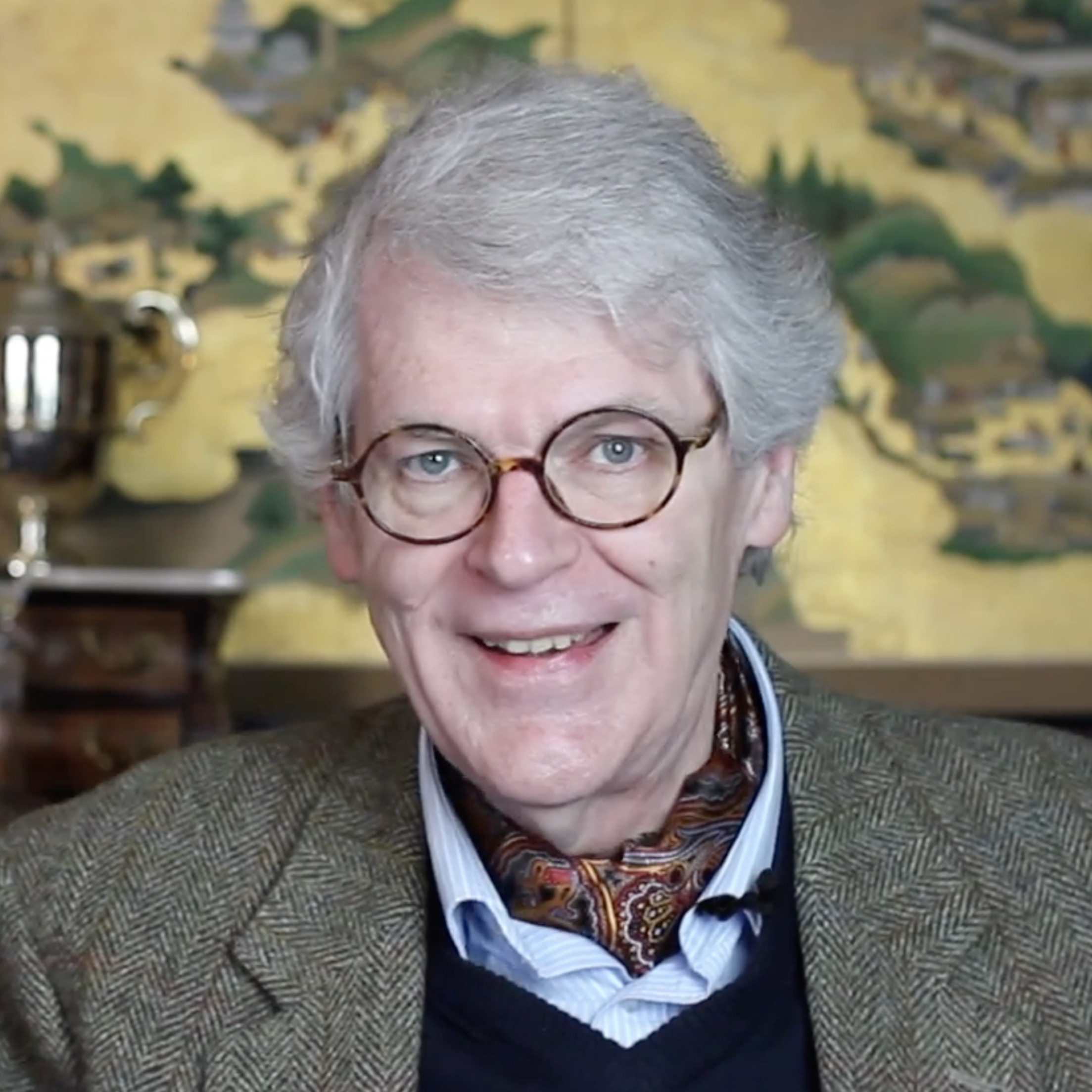
English Literature
Lecture
Critical History (11:46)
Prof. Helen Smith, York University
Bitesize summaries of latest scholarship
Explore the latest scholarship in your subject … 10 minutes a time.
History
Lecture
Reformation and Renaissance (09:56)
Prof. Alec Ryrie, Durham University
Designed specifically for the classroom
Give your students access to a world of knowledge designed specifically for them.
What schools say about us
See all Testimonals
This is the best new resource we have used with students in the last five years.
Head of Humanities
Brighton, Hove & Sussex Sixth Form College

Purchasing MASSOLIT is one of the best decisions we have ever made. We cannot recommend it highly enough.
Head of English
Cherwell School

MASSOLIT is a fabulous resource. We use it within the classroom, as homework and as a flipped learning activity.
Head of English Faculty
Hayesfield Girls’ School & Mixed Sixth Form
















.jpg)





.jpg)
